7. BitBotXL distance sensor
7.1. HC_SR04P

Output a 10µs (µs = microsecond) High signal to Trigger input to start the detection.
Measure the length of pulse received on Echo output to determine distance
Distance is pulse time * speed of sound / 2
The speed of sound is about 343m/s or 34300cm/s or 0.0343 cm/µs (centimeter per microsecond).
Note
µs.µ, which represents 1/1000000, one millionth.utime library us is used instead of µs.Warning
Some objects might not be detected by ultrasonic sensors:
Some objects are shaped or positioned in such a way that the sound wave bounces off the object away from the Ultrasonic sensor.
Some objects are too small to reflect enough of the sound wave back to the sensor to be detected.
Some objects can absorb the sound wave all together (cloth, carpet).
7.2. Ultrasound timing
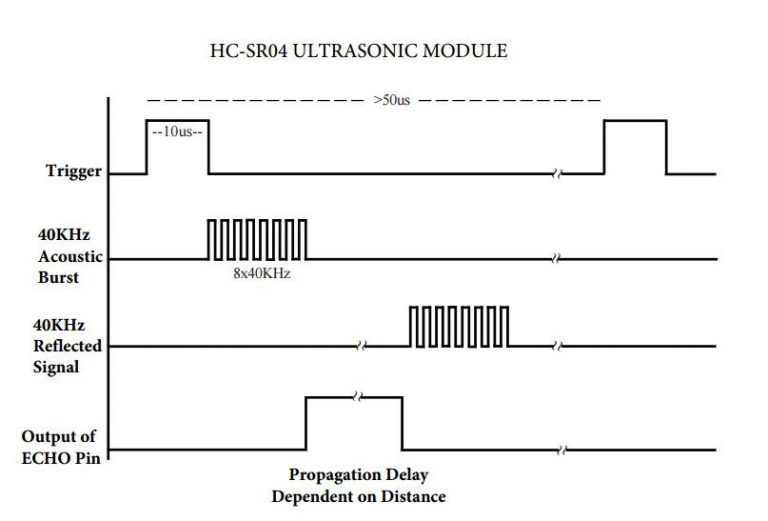
7.3. Trigger pulse
write_digital(1), for 10us, then it is set low, write_digital(0).utime.sleep_us(10).DISTANCE_SENSOR_PIN = pin15, in CAPITALS, can be used to set the pin to be used by the sensor.import utime
DISTANCE_SENSOR_PIN = pin15
DISTANCE_SENSOR_PIN.write_digital(1)
utime.sleep_us(10)
DISTANCE_SENSOR_PIN.write_digital(0)
Once the wave is returned, after being reflected by an object, the Echo pin goes high for a particular amount of time which will be equal to the time taken for the wave to return back to the sensor.
The first step is to record the last low timestamp for Echo (pulse_start) e.g. just before the return signal is received and the pin goes high. A while loop is used to repetitively update the pulse_start time, while read_digital() == 0, until the read_digital() value is no longer 0. This gives the pulse_start time for when read_digital() changes to 1.
while DISTANCE_SENSOR_PIN.read_digital() == 0:
pulse_start = utime.ticks_us()
Once a signal is received, the value changes from low (0) to high (1), and the signal will remain high for the duration of the Echo pulse. Then it will go low again.
The second step is to record the last high timestamp for Echo (pulse_end). e.g. just before the return signal is received and the pin goes low. A while loop is used to repetitively update the pulse_end time, while read_digital() == 1, until the read_digital() value is no longer 1. This gives the pulse_end time for when read_digital() changes to 0.
while DISTANCE_SENSOR_PIN.read_digital() == 1:
pulse_end = utime.ticks_us()
The duration of the pulse is then calculated using pulse_duration = pulse_end - pulse_start.
Since the distance to the object is half of the distance travelled by the pulse to and back from the object, the distance can be calculated using distance = speed x time / 2. The speed is 0.0343 cm/µs. 0.01715 is used instead since 0.0343 / 2 = 0.01715.
pulse_duration = pulse_end - pulse_start
distance = int(0.01715 * pulse_duration)
7.4. class BitBotXLDistanceSensor
class BitBotXLDistanceSensor(), is used for the code related to the ultrasound sensor.def distance(self) which returns the distance in cm.The complete code is:
from microbit import *
import utime
DISTANCE_SENSOR_PIN = pin15
class BitBotXLDistanceSensor():
def distance(self):
DISTANCE_SENSOR_PIN.write_digital(1)
utime.sleep_us(10)
DISTANCE_SENSOR_PIN.write_digital(0)
while DISTANCE_SENSOR_PIN.read_digital() == 0:
pulse_start = utime.ticks_us()
while DISTANCE_SENSOR_PIN.read_digital() == 1:
pulse_end = utime.ticks_us()
pulse_duration = pulse_end - pulse_start
distance = int(0.01715 * pulse_duration)
return distance
7.5. Set up the distance sensors
- class BitBotXLDistanceSensor
- Set up the buggy’s distance sensors for use.Use
distance_sensor = BitBotXL.BitBotXLDistanceSensor()to use the buggy’s distance sensors.
from microbit import *
import BitBotXL
# setup distance_sensor
distance_sensor = BitBotXL.BitBotXLDistanceSensor()
Note that in BitBotXL.BitBotXLDistanceSensor(), BitBotXL is the module and BitBotXLDistanceSensor is the class within it.
7.6. Distance to an object
- distance()
Returns the distance, in cm, to an object.
distance_sensor.distance() to display the distance to objects.from microbit import *
import BitBotXL
distance_sensor = BitBotXL.BitBotXLDistanceSensor()
while True:
d = distance_sensor.distance()
display.scroll(d, delay=60)
distance_sensor.distance() < 50, measures the distance to objects and if the distance is less than 50cm it spins the buggy to the left for 1 second. The code for the buggy motor functions (move_forwards and spin_from_obstacle) is not included below.from microbit import *
import BitBotXL
# setup buggy
buggy = BitBotXL.BitBotXLMotors()
distance_sensor = BitBotXL.BitBotXLDistanceSensor()
while True:
move_forwards(drive_time=200)
# check for obstacle and spin
d = distance_sensor.distance()
if d < 50:
while d < 50:
spin_from_obstacle(spin_time=1000)
d = distance_sensor.distance()
Tasks
Write code to drive the buggy forwards until it measures an object 30cm in front and then stops.
Write code to drive the buggy forwards until it measures an object 20cm in front and then it stops for 500ms, goes backwards for 500ms, then spins, goes forwards and repeats.