2. MiniBit motors
Pins for the motors are below.
Pin |
Purpose |
|---|---|
pin12 |
Left Motor |
pin8 |
Left Motor Backward |
pin14 |
Right Motor |
pin16 |
Right Motor Backward |
2.1. Motor pin constants
LMF = pin12Tasks
Set constants for the 4 motor pins.
from microbit import *
LMF = pin12
LMB = pin8
RMF = pin16
RMB = pin14
2.2. Stop
write_digital(0) to stop the motors controlled by each pin.Tasks
Write code to stop all motors in a def block:
def stop().
from microbit import *
LMF = pin12
LMB = pin8
RMF = pin16
RMB = pin14
def stop():
LMF.write_digital(0)
LMB.write_digital(0)
RMF.write_digital(0)
RMB.write_digital(0)
stop()
2.3. Scaling speeds
(to_value - to_min) / (to_max - to_min) = (from_value - from_min) / (from_max - from_min)).to_value = int(((from_value - from_min) / (from_max - from_min)) * (to_max - to_min) + to_min).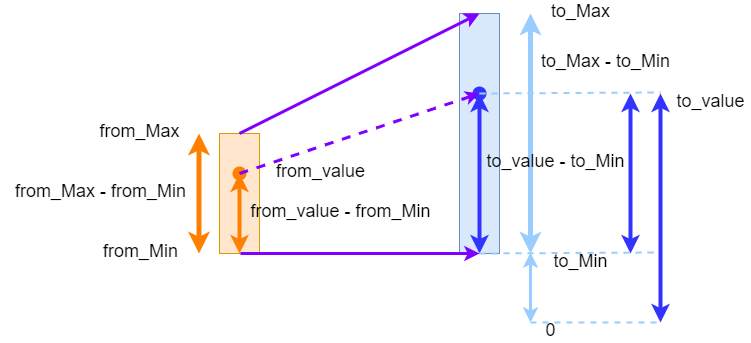
- scale(from_value, from_min, from_max, to_min, to_max)
- Returns a value, from_value, from a range of (from_min, from_max), to an equivalent value in a range of (to_min, to_max).
- speed_scaled(speed)
- Converts a value from a range of (0, 10) to an equivalent value in the range (0, 1023).
from microbit import *
def scale(from_value, from_min, from_max, to_min, to_max):
return int(((from_value - from_min) / (from_max - from_min)) * (to_max - to_min) + to_min)
def speed_scaled(speed):
return scale(speed, 0, 10, 0, 1023)
2.4. Drive forwards
def forwards(speed=2, duration=None).speed_scaled(speed) to convert from a speed in the 0-10 range to an analog_speed.write_analog(analog_speed) to drive the motor where analog_speed is from 0 to 1023.write_digital(0) to stop the other motors.write_digital(0) to turn it off.Tasks
Write code to drive forwards at speed 4 for 2 seconds.
from microbit import *
LMF = pin12
LMB = pin8
RMF = pin16
RMB = pin14
def scale(from_value, from_min, from_max, to_min, to_max):
return int(((from_value - from_min) / (from_max - from_min)) * (to_max - to_min) + to_min)
def speed_scaled(speed):
return scale(speed, 0, 10, 0, 1023)
def forwards(speed=2, duration=None):
analog_speed = speed_scaled(speed)
LMF.write_analog(analog_speed)
LMB.write_digital(0)
RMF.write_analog(analog_speed)
RMB.write_digital(0)
if duration is not None:
utime.sleep_ms(duration)
stop()
forwards(speed=4, duration=2000)
2.5. Drive backwards
def backwards(speed=2, duration=None).Tasks
Write code to drive backwards at speed 3 for 4 seconds.
from microbit import *
LMF = pin12
LMB = pin8
RMF = pin16
RMB = pin14
def scale(from_value, from_min, from_max, to_min, to_max):
return int(((from_value - from_min) / (from_max - from_min)) * (to_max - to_min) + to_min)
def speed_scaled(speed):
return scale(speed, 0, 10, 0, 1023)
def backwards(speed=2, duration=None):
analog_speed = speed_scaled(speed)
LMF.write_digital(0)
LMB.write_analog(analog_speed)
RMF.write_digital(0)
RMB.write_analog(analog_speed)
if duration is not None:
utime.sleep_ms(duration)
stop()
backwards(speed=3, duration=4000)
2.6. Turning calculation for differential motor speeds
inner_turn_speed(speed, tightness=2) that takes the motor speed of the outside wheel and calculates the speed of the inner wheel using a tightness factor.from microbit import *
def inner_turn_speed(speed, tightness=4):
if tightness == 0:
return 0
else:
return int(speed / tightness)
2.7. Turn left
def left(speed=2, tightness=2, duration=None).Tasks
Write code to turn left using a speed of 3, tightness of 2, for a duration of 3000ms.
from microbit import *
LMF = pin12
LMB = pin8
RMF = pin16
RMB = pin14
def scale(from_value, from_min, from_max, to_min, to_max):
return int(((from_value - from_min) / (from_max - from_min)) * (to_max - to_min) + to_min)
def speed_scaled(speed):
return scale(speed, 0, 10, 0, 1023)
def inner_turn_speed(speed, tightness=2):
if tightness == 0:
return 0
else:
return int(speed / tightness)
def left(speed=2, tightness=2, duration=None):
outer_speed = speed_scaled(speed)
inner_speed = inner_turn_speed(outer_speed, tightness)
LMF.write_analog(inner_speed)
LMB.write_digital(0)
RMF.write_analog(outer_speed)
RMB.write_digital(0)
if duration is not None:
utime.sleep_ms(duration)
stop()
left(speed=3, tightness=2, duration=3000)
2.8. Turn left forwards or backwards
Tasks
Write code to turn forwards and backwards to the left using: speed=3, tightness=4, duration=2000.
from microbit import *
LMF = pin12
LMB = pin8
RMF = pin16
RMB = pin14
def scale(from_value, from_min, from_max, to_min, to_max):
return int(((from_value - from_min) / (from_max - from_min)) * (to_max - to_min) + to_min)
def speed_scaled(speed):
return scale(speed, 0, 10, 0, 1023)
def inner_turn_speed(speed, tightness=2):
if tightness == 0:
return 0
else:
return int(speed / tightness)
def left(speed=2, tightness=2, duration=None):
outer_speed = speed_scaled(speed)
inner_speed = inner_turn_speed(outer_speed, tightness)
if speed > 0:
LMF.write_analog(inner_speed)
LMB.write_digital(0)
RMF.write_analog(outer_speed)
RMB.write_digital(0)
else:
LMF.write_digital(0)
LMB.write_analog(-inner_speed)
RMF.write_digital(0)
RMB.write_analog(-outer_speed)
if duration is not None:
utime.sleep_ms(duration)
stop()
while True:
left(speed=3, tightness=4, duration=2000)
left(speed=-3, tightness=4, duration=2000)
2.9. Turn right forwards or backwards
def right(speed=2, tightness=2, duration=None).Tasks
Write code to turn forwards and backwards to the right using: speed=4, tightness=3, duration=2000.
from microbit import *
LMF = pin12
LMB = pin8
RMF = pin16
RMB = pin14
def scale(from_value, from_min, from_max, to_min, to_max):
return int(((from_value - from_min) / (from_max - from_min)) * (to_max - to_min) + to_min)
def speed_scaled(speed):
return scale(speed, 0, 10, 0, 1023)
def inner_turn_speed(speed, tightness=2):
if tightness == 0:
return 0
else:
return int(speed / tightness)
def right(speed=2, tightness=2, duration=None):
outer_speed = speed_scaled(speed)
inner_speed = inner_turn_speed(outer_speed, tightness)
if speed > 0:
LMF.write_analog(outer_speed)
LMB.write_digital(0)
RMF.write_analog(inner_speed)
RMB.write_digital(0)
else:
LMF.write_digital(0)
LMB.write_analog(-outer_speed)
RMF.write_digital(0)
RMB.write_analog(-inner_speed)
if duration is not None:
utime.sleep_ms(duration)
stop()
while True:
right(speed=4, tightness=3, duration=2000)
right(speed=-4, tightness=3, duration=2000)
2.10. Spin left
def spin_left(speed=, duration=None).Tasks
Write code to turn spin left using: speed=4, duration=2000.
from microbit import *
LMF = pin12
LMB = pin8
RMF = pin16
RMB = pin14
def scale(from_value, from_min, from_max, to_min, to_max):
return int(((from_value - from_min) / (from_max - from_min)) * (to_max - to_min) + to_min)
def speed_scaled(speed):
return scale(speed, 0, 10, 0, 1023)
def spin_left(speed=2, duration=None):
analog_speed = speed_scaled(speed)
LMF.write_digital(0)
LMB.write_analog(analog_speed)
RMF.write_analog(analog_speed)
RMB.write_digital(0)
if duration is not None:
utime.sleep_ms(duration)
stop()
spin_left(speed=4, duration=2000)
2.11. Spin right
def spin_right(speed=2, duration=None).Tasks
Write code to turn spin right using: speed=3, duration=3000.
from microbit import *
LMF = pin12
LMB = pin8
RMF = pin16
RMB = pin14
def scale(from_value, from_min, from_max, to_min, to_max):
return int(((from_value - from_min) / (from_max - from_min)) * (to_max - to_min) + to_min)
def speed_scaled(speed):
return scale(speed, 0, 10, 0, 1023)
def spin_right(speed=2, duration=None):
analog_speed = speed_scaled(speed)
LMF.write_analog(analog_speed)
LMB.write_digital(0)
RMF.write_digital(0)
RMB.write_analog(analog_speed)
if duration is not None:
utime.sleep_ms(duration)
stop()
spin_right(speed=3, duration=3000)